Transient heat flow simulation in SIMU-THERM 8.0
In a transient simulation the inside and outside thermal conditions (temperature, heat transfer..) are not constant (unlike in the steady state case)
Temperature and heat transfer are given as curves over time.
When is transient simulation needed ?
- Simulation of heating and cooling a plant, e.g. to get a better estimation of the power needed to heat up a furnace.
- Drying simulation for fire concrete walls
- Simulation of metal gutters
- Simulation of fire protection systems
- Many devices are operated cyclically and thus never get into a steady state.
Examples for this: Cyclically operated furnaces, transportation containers, metal ladles, kiln cars.
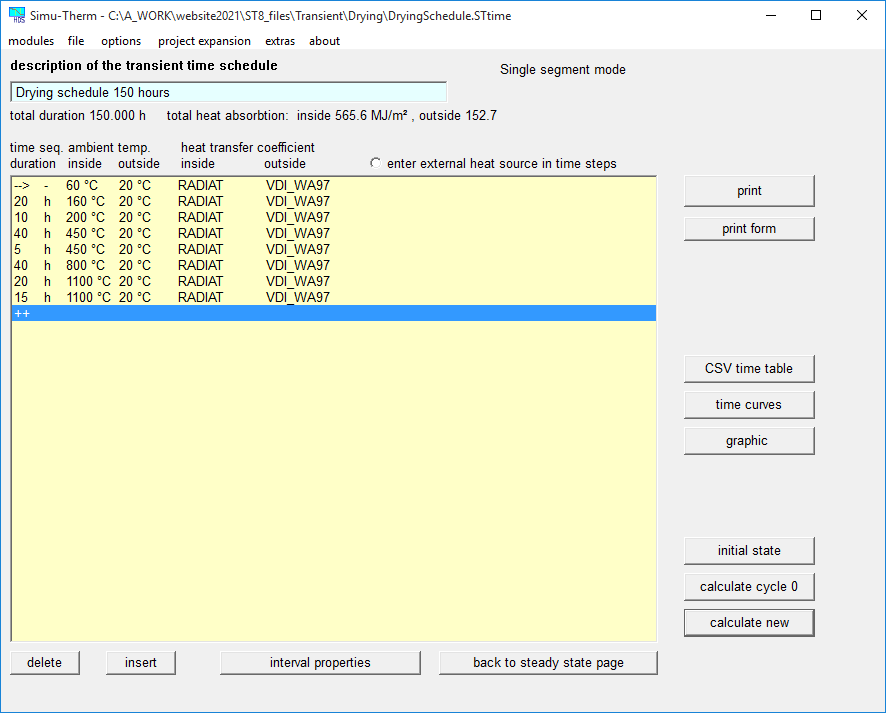
Transient dialogs in SIMU-THERM
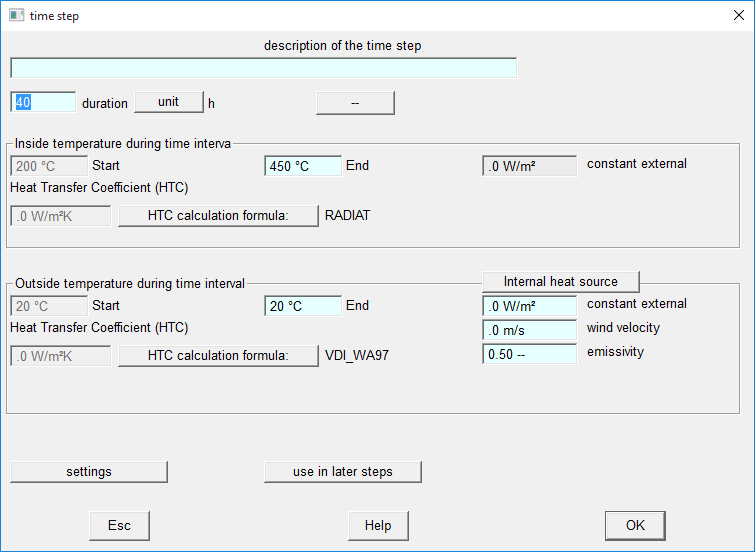
In the transient main dialog a time schedule of thermal conditions is defined.
The time schedule (e.g a heating schedule or drying schedule) can be applied to any steady state calculation and it is stored in separate files.
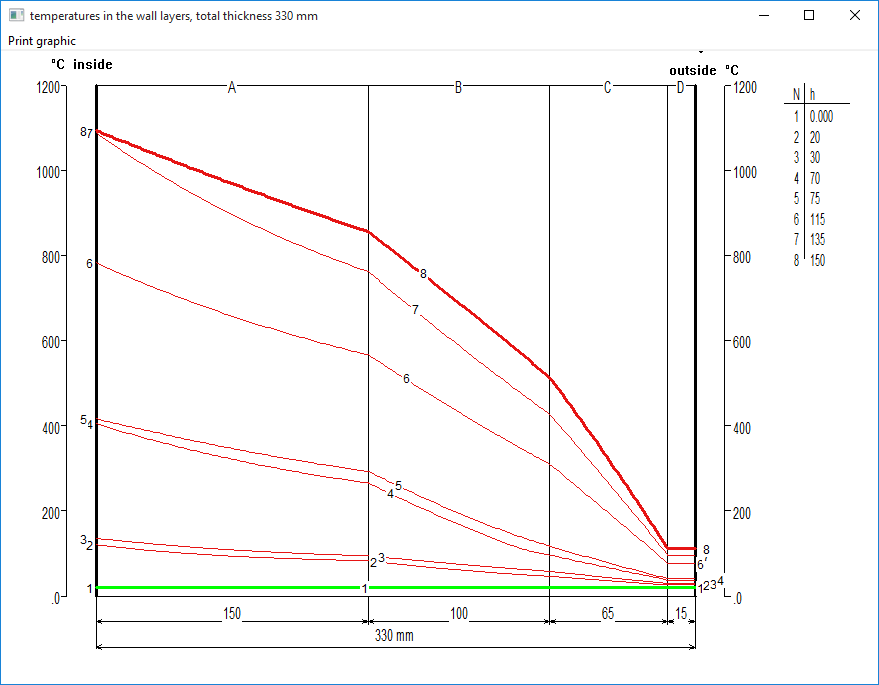
The basic result of a transient simulation is the wall temperature graph.
The green line represents the initial wall temperature (at the beginning of the simulation)
The fat red line is the temperature at the end of the simulation
Thin red lines show the temperature at the time steps in between, defined by the user.
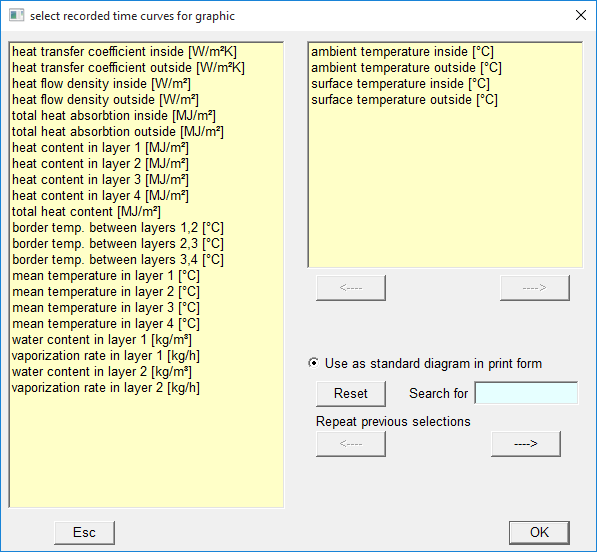
Time curves of recorded results
During the simulation several figures are recorded for every time step.
In the curve selection dialog arbitrary combinations of the curves can be selected and shown as diagrams over time.
Here some typical examples of diagrams:
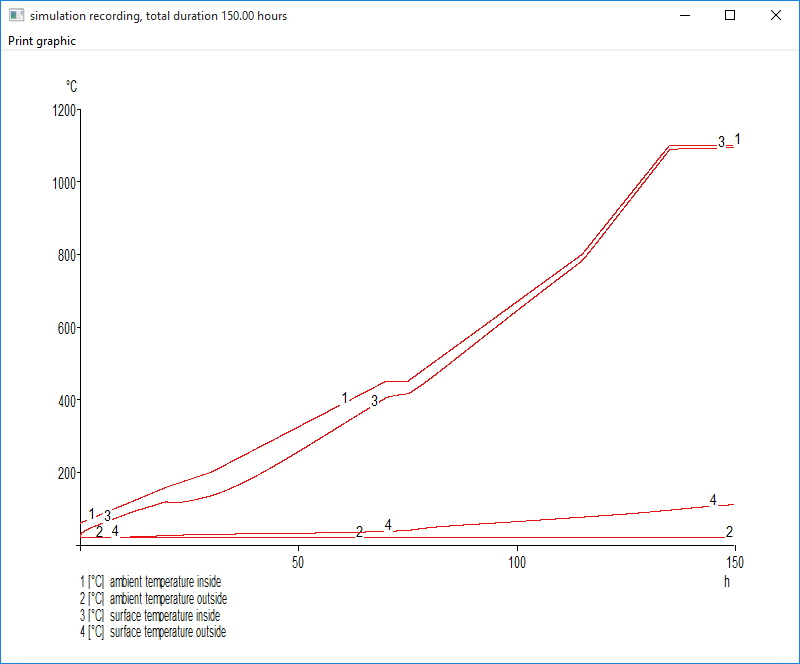
- Ambient temperature and surface temperature, both inside and outside
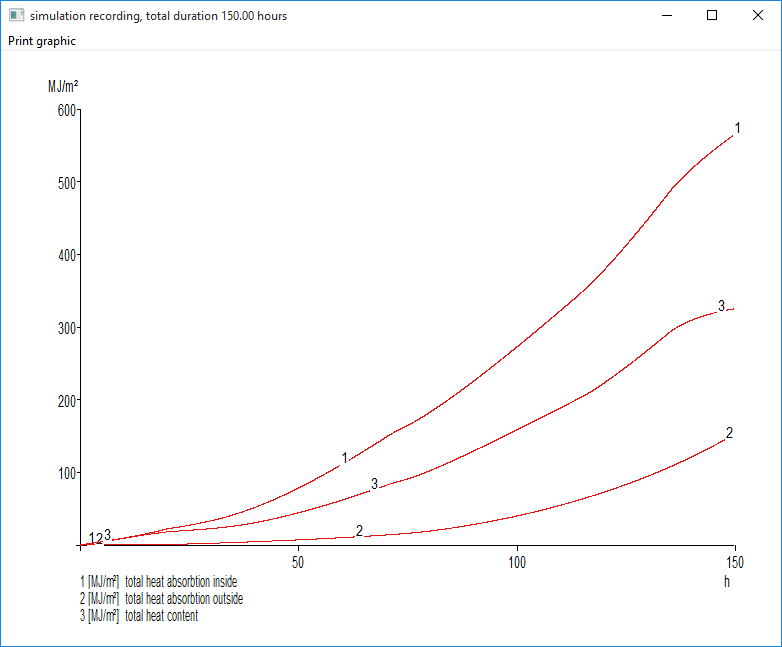
- Heat absorption and heat content of the wall
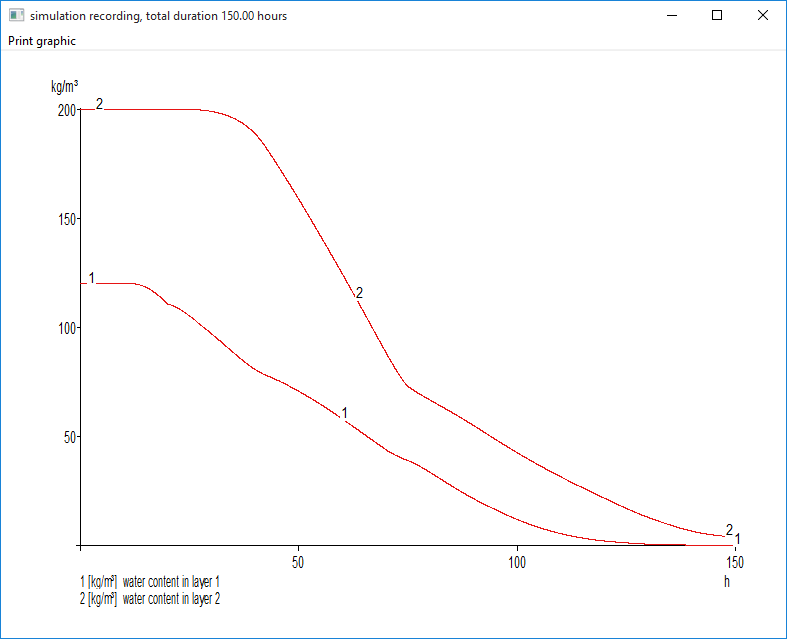
- Water content of the concrete wall layers
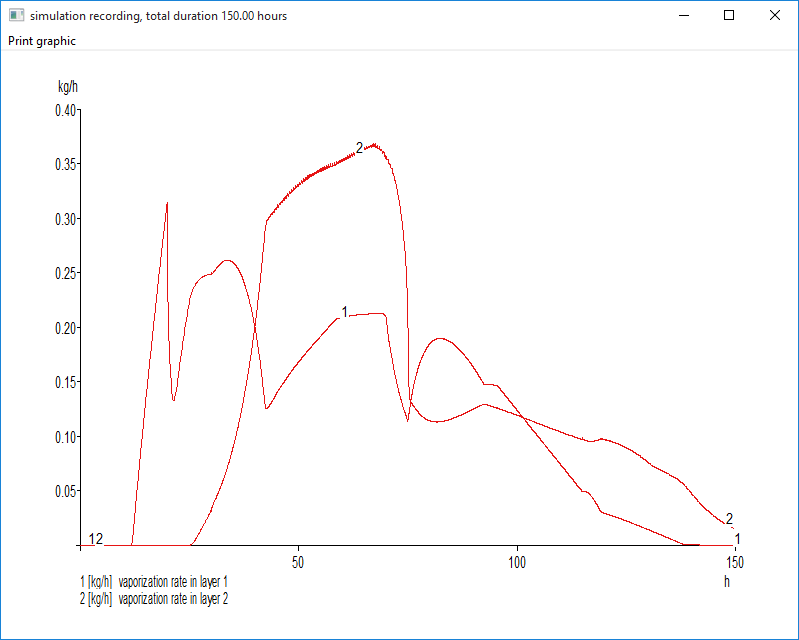
- Water vaporization rate